Privacy and security in the Age of AI : Safeguarding Data in Smart Systems
- Posted by Deepak Shukla
- Categories Blog, College, Corporate, Individual, Trainers
- Date April 20, 2024

Privacy and security in the Age of AI : Safeguarding Data in Smart Systems
Privacy and security in the Age of AI are paramount considerations as smart systems become increasingly pervasive. Here are some key strategies for safeguarding data in these environments:
Data Minimization: This principle advocates for collecting only the data absolutely necessary for a specific purpose. By limiting the amount of data collected, organizations can minimize the volume of data potentially exposed in a security breach. This not only reduces risk but also simplifies data management and storage requirements.
Encryption: Encryption is a fundamental security measure that encodes data, allowing only authorized parties to decode and read it. Using strong encryption protocols for data at rest and in transit ensures that intercepted data remains inaccessible and unreadable without the decryption key, significantly enhancing data security.
Access Control: Access control mechanisms restrict data access exclusively to those who need it to perform their job functions. Implementing role-based access control (RBAC) assigns permissions based on roles within an organization, minimizing unnecessary access and potential data exposure. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) secures systems further by requiring users to verify their identity in multiple ways before accessing sensitive data.
Privacy enhancing and Data masking: These techniques modify personal data so that individuals cannot be identified without additional information kept separately. Anonymization permanently removes personally identifiable information, making re-identification impossible. Pseudonymization substitutes private identifiers with artificial identifiers or pseudonyms, both methods significantly protecting personal data and reducing risks during data processing and storage.
Privacy by Design: This approach integrates privacy and data protection features from the start of designing AI systems and throughout their lifecycle. This proactive stance ensures that data protection is a core consideration from the outset, not an afterthought.
Transparency and Consent: Being transparent about how you collect data and ensuring that users give informed consent before collection builds trust and complies with legal standards. Clearly explain how, why, and what data will be used for, and provide users the option to opt out if they disagree with the data usage terms.
Regular Audits and Assessments: Performing regular security audits and risk assessments helps organizations identify vulnerabilities in their AI systems and data processes. This proactive approach enables timely detection and rectification of security gaps, helping to avert breaches before they happen.
Data Breach Response Plan: Developing a clear plan for responding to data breaches includes setting up immediate action steps to control and mitigate damage, along with procedures for notifying affected parties and strategies to prevent future incidents. Swift and transparent communication plays a crucial role in effectively managing the situation and maintaining public trust.
Secure Development Practices: Maintaining security should be a priority throughout the development lifecycle of software and AI systems. This includes adhering to secure coding practices, regularly updating and patching software to fix vulnerabilities, and conducting security testing to ensure a robust defence against attacks.
Collaboration and Information Sharing: Engaging in partnerships and information-sharing initiatives with other organizations enhances security measures. Sharing knowledge and best practices about threats and defensive mechanisms allows the community to collectively strengthen its defences against common and emerging security challenges.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can better protect their data in AI applications and systems, thereby reducing risks and adapting effectively to the evolving landscape of cyber threats and regulatory requirements.
For more related info about AI in future check the link given below:
The Future of Work: How AI is Shaping New Careers
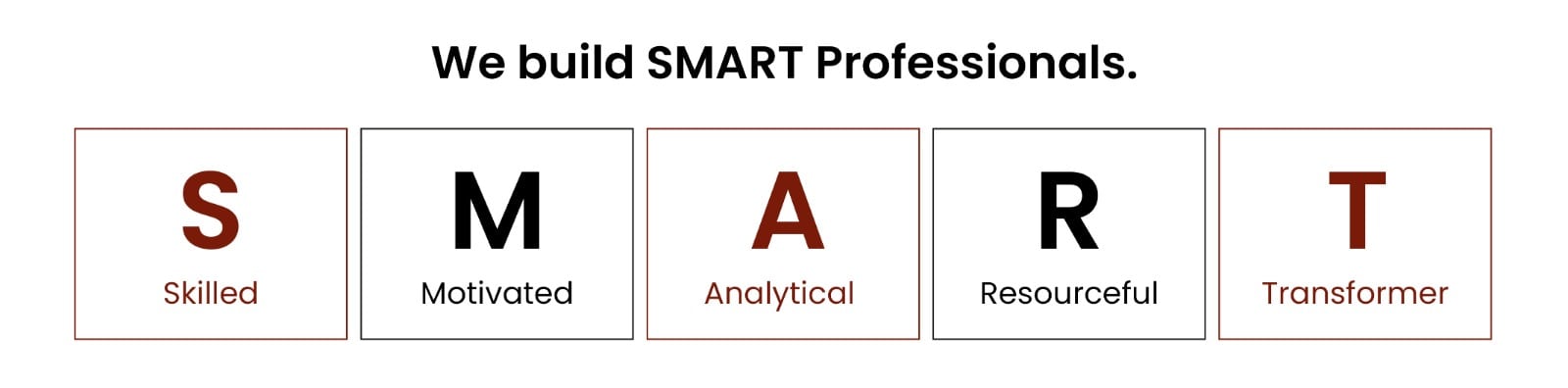
About the Author: Deepak Shukla Is Digital marketing and sales coordinator at IDI Institute de Informatica. Learning for career is an Initiative of IDI that conducts courses in futuristic technologies with an aim to build SMART professionals where SMART means Skilled, Motivated, Analytical, Resourceful and Transform people.
You may also like
AI Career Explosion: 50 Top Jobs Awaiting You
In the ever-evolving world of technology, Generative AI stands out as one of the most groundbreaking advancements.
Edge Computing: A Revolution at the Network’s Frontier
In the ever-evolving world of technology, Generative AI stands out as one of the most groundbreaking advancements.
From GPT-1 to GPT-4: The AI Language Revolution
In the ever-evolving world of technology, Generative AI stands out as one of the most groundbreaking advancements.